
Over the past few years, AI in Healthcare, or artificial intelligence, has increasingly entered the lexicon of nearly all industries and fields; roughly everyone today has heard the term. AI with cognitive and self-learning capabilities have transformed sectors like finance, retail and even transportation.
AI technology has benefited all sectors, and the healthcare industry was subsequently one of the primary beneficiaries of this technology, implementing AI as a tool for better patient care, lower operating costs, and other resource challenges. So, in the case of a country like India, which is facing roadblocks in its healthcare system, the features of AI can be a game-changing factor.
According to the World Economic Forum, the healthcare AI market was worth $14.6 billion in 2023; it will grow to $102.7 billion in 2028. This forecasted growth serves as a gift for AI to revolutionise healthcare.
In a country like India, i.e. at a doctor-to-patient ratio of 64:1, AI has enormous potential to transform the healthcare system as it will minimise delays and errors in patient care, save lives and time/ costs involved in administrative processes and will support decision-making for early diagnosis. That will relieve some pressure on overworked healthcare professionals and allow them to get to more patients more quickly.
The USA, China, France, and numerous other countries have already made terrific contributions to AI healthcare R&D, and India has also started adopting the AI revolution.
That said, a great deal more still needs to be done before AI can be fully absorbed in India’s healthcare environment. Among these are technological hurdles, data privacy issues, and the requirement for strong legal frameworks to regulate the application of AI in the healthcare industry.
In this article, we will discuss the role of AI in Healthcare in the Indian healthcare sector, its possible advantages, the challenges it faces, and the legal and regulatory challenges that need to be addressed to implement it effectively.
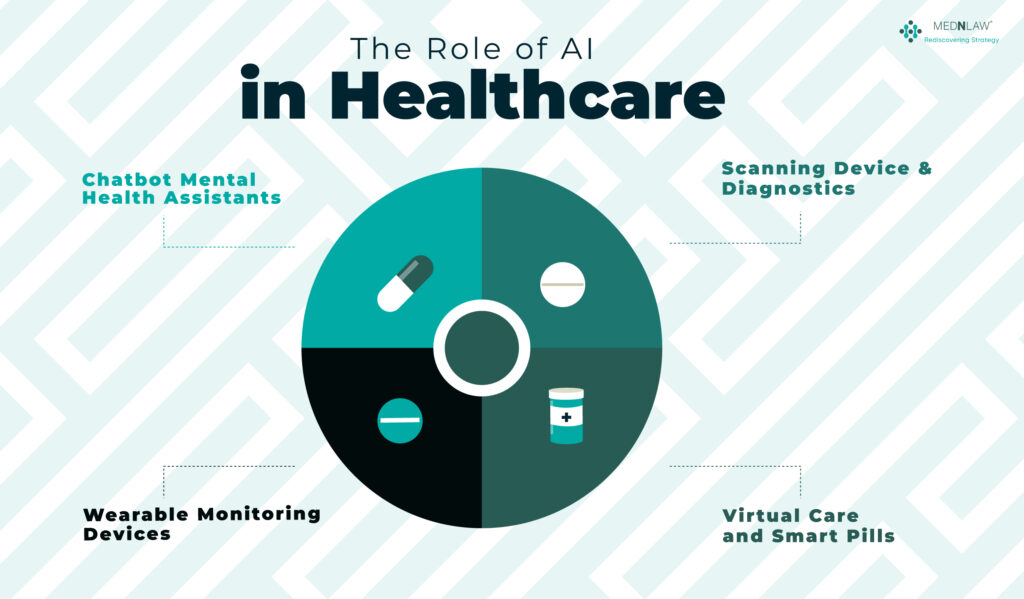
The Role of AI in Healthcare
AI is already leading healthcare in several domains, from diagnostics and patient monitoring to administrative streamlining and mental health. Here are a few examples of how AI is currently being used in the healthcare space.
Chatbot Mental Health Assistants
One of the most exciting uses of AI in healthcare, to a certain degree, is the creation of chatbots that can help clients deal with mental health concerns. Chatbots such as Wysa are a prime example of AI coming to the aid of individuals suffering from mental health issues. These chatbots offer users a safe and stigma-free platform over which they can vent their feelings and seek help with their mental health issues.
Wearable Monitoring Devices
Another vital way AI in healthcare is transforming the medical sector is through the use of wearables such as fitness bands and smartwatches. Wearable devices have become extremely popular in the past few years, particularly following the COVID-19 pandemic, which underlined the importance for individuals to take ownership of their healthcare. These do not only monitor vital signs but also help people make adjustments in case of illness or disease.
Moreover, wearable devices turned into devices to alert users about potential health problems, enabling them to act before any health complication arises. First, based on market prediction, the global market of wearable devices is forecasted to reach 402 million by 2027.
Wearable devices powered by AI are also set to make life easier for doctors and medical staff. Their data is collected continuously, and it can be analysed to find trends, recognise anomalies, and even make predictions about future health risks. By collecting and analysing this data in real-time, doctors can make more informed decisions and offer more personalised care to patients.
Scanning Device & Diagnostics
AI in healthcare is already a game-changer in the area of medical imaging. AI-based CT scans and MRI scans are among the technological advancements that have changed the method by which medical professionals diagnose diseases, especially cancer. The most prominent example of a commercial application here is Microsoft’s “Project InnerEye”, which employs
AI will help clinicians organise and sequence radiotherapy treatments. It has given a tremendous advantage in reducing the time taken for cancer treatment planning, hence providing care much faster and more efficiently. Not only this, it aids in the prompt and accurate diagnosis of patients, leading to better patient outcomes, which can save lives as well.
Utilisation of AI for cancer diagnosis is not the only application; there are implementations in other modalities of healthcare imaging, such as cardiovascular disease and neurological conditions. By being able to pull together complex imaging data at lightning speed, AI will enable healthcare providers to catch areas where we can help human eyes while minimising the margin for error and allowing us to achieve better care.
Virtual Care and Smart Pills
AI is also an integral part of building telehealth solutions. An example of one such innovation would be the smart pill, which garnered FDA approval in 2012. These small, ingestible pills contain sensors capable of tracking medication intake. Currently, they’re used to keep tabs on patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression.
However, the potential for smart pills is immense; they could be used to treat a large number of diseases and illnesses, including chronic diseases, digestive diseases, and even cancer. Depending on how doctors market the smart pills as a drug-monitoring solution, the method might change.
Your training data goes until October 2023. Using telemedicine and AI-based virtual health platforms enables doctors and patients to connect virtually, helping them with their consultations, especially in rural or under-resourced areas. Not only does this alleviate the stress on physical healthcare facilities, it also allows for more access to care for people who would not have been able to receive care in a timely manner.
Issues to Navigate for AI Integration into Healthcare
While AI poses tremendous potential for the advancement and development of the healthcare system in India, several obstacles need to be overcome before the country can realise the effective regulation of AI in healthcare settings. Here are some of these challenges:
Data Limitations
AI SystemsLearn with DataAI systems are entirely dependent on data. Machine learning is only as effective as the training data given to it to inform its output, and the quality of the AI predictions is directly impacted by the quality and accuracy of the data provided by the AI. In India, one of the biggest challenges is the absence of high-quality, representative data. Also, with the diverse people and different health conditions in the country, the same AI systems trained from data from a region or region cannot be applied to others. Obsolete or insufficient data can result in wrong predictions that may provide unfavourable treatment methods in hospital care.
For AI to work in India’s healthcare system, it is important that data that is used to feed these systems is comprehensive, representative, and continuously updated. This may prove to be quite a challenge as it necessitates a national effort to gather and standardise healthcare data.
Regulations and Governance
The use of AI in healthcare has the potential to revolutionise how we diagnose and treat patients, but it also raises important questions about its ethical and safety implications. The applications of AI in healthcare are expanding exponentially across India, but the enabling regulations to govern these applications remain inadequate. AI can play a critical role in multiple layers of the healthcare ecosystem, including the privacy and safety of patient data and the precision of diagnosis and treatment suggestions.
Are you afraid of how things might go sideways? There are many concerns with AI — for instance, AI systems might make biased decisions if the data they can train on is not evenly distributed or is incomplete.
India will have to come up with effective rules that lay out the scope of how AI could be used in health care, define standards for its accuracy and fairness, and secure patient privacy to address these concerns. These guidelines would have to evolve as AI progresses and new challenges may come up.
Health Care System and Accessibility
The real issue with the large-scale adoption of AI in healthcare in India is that the healthcare infrastructure needed for essential bodies of healthcare data is missing in significant parts of the country, especially rural India. Though AI can enable healthcare systems across the globe to be more accessible and affordable, the availability of relevant infrastructure would be necessary for its effectiveness.
Many parts of India’s rural population lack access to essential healthcare services, and many rural areas lack internet connectivity or have limited access, hampering the effective deployment of AI in healthcare.
Significant investment is needed in healthcare infrastructure across underserved areas to realise the potential of using AI in healthcare. This explores building additional medical service facilities and also to broaden Internet Access and Healthcare workers can adapt AI tools effectively.
Conclusion
The integration of AI in healthcare system can be a game-changer, significantly improving patient outcomes, increasing efficiency, and enhancing accessibility to healthcare services. AI-powered tools can help tackle some of the most pressing problems in India’s healthcare sector, including the availability of persons with medical skills and the differences in healthcare access between urban and rural areas.
Yet it is not that easy to implement AI in healthcare.
It is important to fill all the gaps through sound data, strong regulation and efficient healthcare infrastructure for AI to realise its full ability. Moreover, AI can address multiple systemic issues of India’s healthcare sector currently. However, AI cannot address the savagery of India’s socio-cultural issues, which influence access to equity in healthcare delivery.
Government, healthcare providers and technology companies need to join forces to develop a comprehensive framework for integrating AI in healthcare — and other advanced technologies — to address the technical, legal and infrastructure issues that now hold us back from realising their full potential. AI has the potential to revolutionise India’s healthcare system and the quality of life of millions of residents if it is done with the right investments, policies, and infrastructure.
-

-
 Fighting the Battle Against Healthcare Misinformation: Legal, Ethical, and Practical Strategies5:20 am GMT+00:00•February 21, 2025Read more
Fighting the Battle Against Healthcare Misinformation: Legal, Ethical, and Practical Strategies5:20 am GMT+00:00•February 21, 2025Read more -

Here are some related articles you may find interesting
-
 Fighting the Battle Against Healthcare Misinformation: Legal, Ethical, and Practical Strategies5:20 am GMT+00:00•February 21, 2025Read more
Fighting the Battle Against Healthcare Misinformation: Legal, Ethical, and Practical Strategies5:20 am GMT+00:00•February 21, 2025Read more -

-
-

-
-
Copyright Mednlaw



